Litjens G, Kooi T, Bejnordi B E, et al. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1702.05747, 2017.
1. Overview
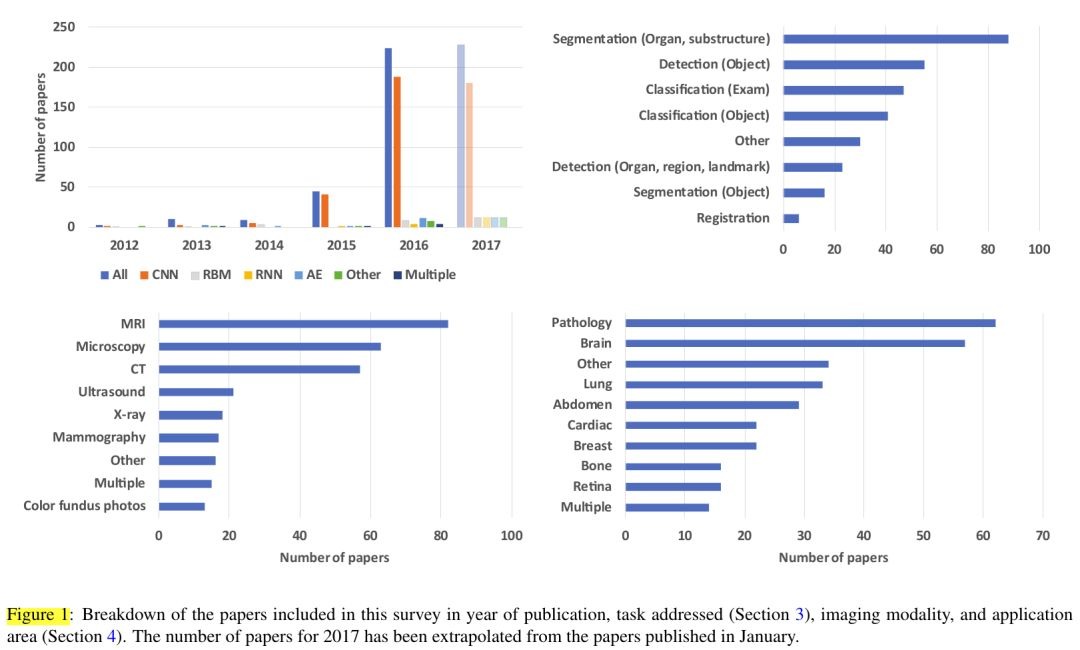
论文检索并分析了308篇与深度学习和医学图像有关的论文。
1.1. 检索方式
- 对PubMed数据库(标题摘要)进行关键词(convolutional or deep learning)检索
- ArXiv检索medical imaging
- MICCAI, SPIE, ISBI, EMBC conference proceeding
1.2. 相关任务
- image classification
- object detection
- segmentation
- registration
- retrieval
- generation
- enhancement
1.3. 应用领域
- neuro
- retinal(视网膜)
- pulmonary(肺)
- digital pathology(病理学)
- breast(乳腺)
- cardiac(心脏)
- abdominal(腹部)
- musculoskeletal(肌肉骨骼)
1.4. CNN Architecture
- Classification Architecture
- Multi-stream Architecture (multi-scale; 2.5D, multiple angled patched from 3D space)
- Segmentation Architecture (U-Net)
1.5. RNN
- pixelRNN for segmentation
1.6. Unsupervised Model
- AE, SAE (AE+AE+…+AE). for denoising
- RBM, DBN (RBM+RBM+…+RBM). 无监督训练,再加上分类器fine tuing
- VAE, GAN
1.7. 数据集
- OASIS. brain MRI registration
- BRATS, LSLES, and MRBrains challenges. brain lesion segmentation
- Kaggle Diabetic Retinopathy challenge 2015. disbetic retinopathy classification
- PROMISE12 challenge. prostate segmentation
- LUNA16 challenge. nodule classification
- CAMELYON16, TUPAC, DREAM. breast cancer metastases detection in lymph nodes
- ICPR 2012, AMIDA 2013, GLAS. gland segmentation
- SLIVER07. liver segmentation
- LIDC-IDRI. detect nodules in lung CT

2. 医学图像中的深度学习应用
2.1. Classification
2.1.1. Image/Exam Classification (图像->是否病变)
使用预训练权重(迁移学习)
- 预训练网络提取特征,作为后续模型输入
- 使用medical数据fine tuning预训练网络
2015~2017年,47篇exam classification paper, 36篇使用CNN, 5篇使用AE, 6篇使用RBM. 且涉及不同的医学领域:retinal, digital pathology, lung computed tomography.
2.1.2. Object or Lesion Classification
对图像中已经识别出来的某个小部分进行多分类(病变类型, nodule classification in chest CT)。通常需要考虑(Multi-stream)
- 病变外观的局部信息
- 病变位置的全局上下文信息
到达高分类准确度。
2.2. Detection
2.2.1. Organ, Region and Landmark Localization
通常需要处理3D图像,一些方法将3D空间看做由一些2D正交平面构成(2D MRI slices)。
图像localization方法分为
- RoI
- 直接regress
此外,还涉及到temporal数据的scan plane or key frame localization (standardized scan planes in mid-pregnancy fetal US).
2.2.2. Object or Lesion Detection
定位并识别lesion (multi-stream for CT and PET data; micro-bleed in brain MRI)
2.3. Segmentation
2.3.1. Organ and Substructure Segmentation
Contour or interior of objects (pectoral muscle in breast MRI, coronary arteries in cardiac CT angiography, vertebral body in MRI).
相关技术
- 2D U-Net
- 3D V-Net, Dice coefficient
- 基于RNN,融合双向信息(left/top, right/bottom)
- 结合双向LSTM和2D U-Net
- 结合FCN和graphical model (MRF, CRF)
2.3.2. Lesion Segmentation
包含
- Object detection
- Organ and substructure segmentation
需要考虑global and loval context [Multi-stream] (white matter lesions in brain MRI).
2.4. Registration
spatial alignment. 包含两种方法
- 估计两张图像的相似度
- 预测transformation parameters
2.5. Other Task
2.5.1. Retrieval
使用Hashing forest进行压缩
2.5.2. Generation and Enhancement
超分辨率
2.5.3. Combine Image with Report
Caption, LDA
Mammography中的3个描述
- shape
- margin
- density
3. 应用领域
3.1. Brain
Alzheimer classification, brain tissue segmentation, anatomical structure (hippocampus).
相关技术
- multi-scale for contextual
- 2D slice-by-slice处理3D数据
3.2. Eye
color fundus imaging (CFI).
3.3. Chest
基于CT扫描估计lung cancer概率
3.4. Digital Pathology and Microscopy
whole-slide images (WSI)
- 检测、分割、分类nuclei
- 分割organ
- 检测分类 the disease of interest at the lesion or WSI-level
3.5. Breast
考虑三个子任务
- 检测分类mass-like lesion
- 检测分类micro-calcfication
- breast cancer评估
3.6. Cardiac
使用2D CNN slice by slice处理3D或4D数据。
3.7. Abdomen
3.8. Musculoskeletal
3.9. Other
4. 总结
4.1. Overview
- prefer end-to-end CNN
4.2. Key Aspect
- data preprocessing or augmentation(相同模型结构,不同结果)
- 针对特定任务的模型结构(multi-view, multi-scale)
- 增加patch size观察更多context
- 超参数(LR, Dropout rate)
4.3. Challenge
- 医学图像数据已有很多,挑战在于图像的标注(需要领域专家进行标注、3D图像标注成本大)。因此,从有限数据进行高效学习是重要的研究方向。 一些研究利用sparse 2D segmentation训练3D segmentation、一些考虑 non-expert labels via crowd-sourcing
- Label noise. 多专家分别进行标注,对比结果是否一致
- Fail in rare category
- Class imbalance. 研究方向(通常对较少样本进行scale, rotate操作)
- 结合patient history, age, demographics进行诊断
- Balance image feature (thousands) and clinical feature (handful)
- patch不具有全局位置信息,而entire image占用较大内存
4.4. Outlook
- Unsupervised, VAE, GAN are attractive
- Combine Bayesian statistic with deep learning
- Image reconstruction (unexplored area)